ETP treats the waste materials into neutralized molecules or reduces the harmful ingredients. Industrial wastewater treatment covers the mechanisms and processes used to treat waters that have been contaminated in some way by anthropogenic industrial or commercial activities prior to its release into the environment or its re-use.
In textile mills, the wastewater effluent contains:
- Organic matter
- Inorganic matter
- Dissolved solids
- Suspended solids
- Dyes
- Chemicals & Auxiliaries
- Metal toxicants
They directly or indirectly effect the colour, alkalinity, pH, hardness, BOD, COD values of water.
What are the sources of wastewater in Textile mills?
The main sources of wastewater from the textile process are:
- Finishing
- Printing
- Bleaching
- Dyeing
- washing
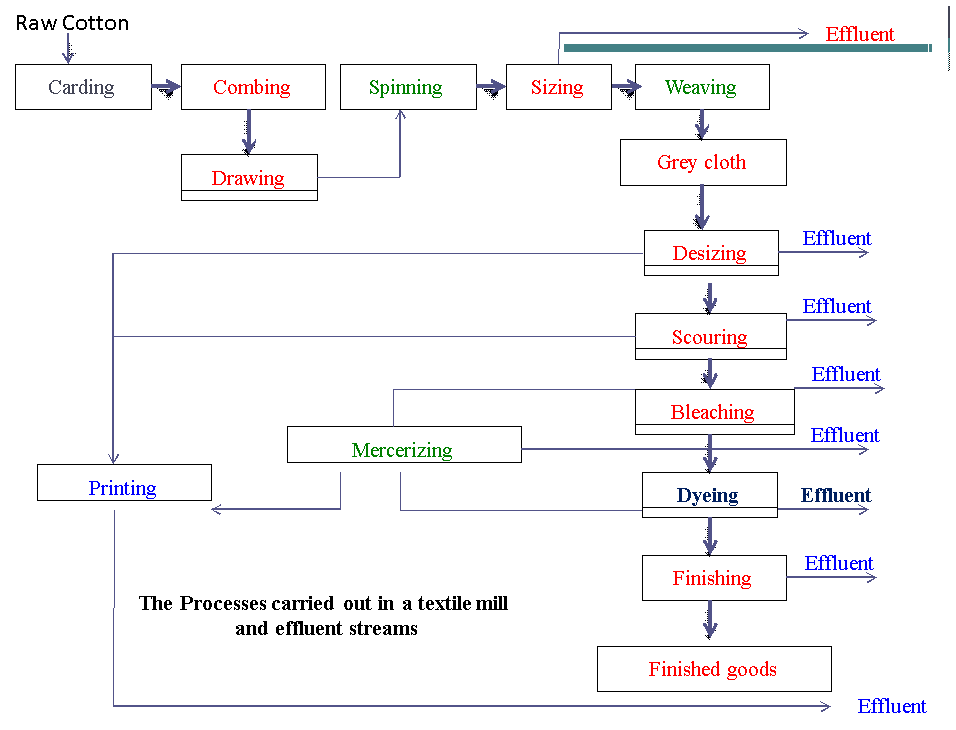
Why treat wastewater?
Wastewater released from textile processing units is treated in an effluent treatment plant (ETP) due to several reasons as follows:
- Basic aim is Environmental protection
- Legal requirement
- Customers requirement
- Corporate social responsibility
- Societal requirement
- Maintenance of clean water
- Conservation and protection of water for industrial and agricultural uses
Categories of Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) Processes
By nature
There are three (3) Categories by nature of the treatment being used in sewage treatment plant as follows:
- Physical
- Chemical
- Biological
By degree of treatment:
There are 4 main types of treatment in wastewater treatment plants by the degree of treatment as follows:
- Preliminary treatment
- Primary treatment
- Secondary treatment
- Tertiary/advanced treatment
Categories of treatment in Degree of treatment do have physical, chemical, biological processes in them.
- Preliminary treatment is mostly physical treatment
- Primary treatment may contain both physical and biological treatment
- Secondary treatment also known as biological treatment
- Tertiary treatment contains both chemical and biological processes
Above mentioned treatment processes further, contain below-mentioned processes in table
| Preliminary Treatment | Primary Treatment |
| Screening Scraper Grit chamber Skimming tank Aeration | Sedimentation Clarification Flocculation ETP Equalization Tank Neutralization tank |
| Secondary Treatment | Tertiary Treatment |
| Activated Sludge Process Trickling filter Aerated Lagoons Oxidation Pond | Sand filters Activated carbon filters Disinfection Ion-exchange Nutrient removal |
Preliminary Treatment
Preliminary treatment wastewater treatment plants get rid of overweight solids and materials that can be easily collected from the effluent and can harm or choke the pumps and skimmers of primary treatment clarifiers. These are in-organic materials and insoluble organic pollutants (i.e. huge floating and suspended solid material, gravel, oil & grease) which are inert and cause problems to further chemical and biological treatments. The presence and sequence of preliminary treatment units totally depend on the characteristics of effluent that is to be treated. All preliminary treatment consists of physical separation techniques by controlling flow rate of effluent. The physical separation techniques are as follows:
Screening:
The influent sewage water is screened to remove all large objects like fabric parts, plastic packets, or any other container etc. According to size of the solid particles to be removed there are further three main types of screens
- Bar Screens
- Course Screens
- Fine Screens

Scraper:
The purpose of a scraper wastewater treatment plants is to remove solids, produce a cleaner effluent and concentrate solids. Concentration of solids removed from the wastewater reduces the volume of sludge for dewatering and/or disposal.

Grit Chamber:
Grit chambers in wastewater treatment plants are long narrow tanks that are designed to slow down the flow so that solids particles will settle out of the water. When waste flows into the grit chamber, particles settle down to the bottom of the chamber based on their size, their specific gravity, and the speed of roll in the tank

Skimming Tank:
A skimming tank in wastewater treatment plants is a chamber designed so that floating matter rises and remains on the surface of the wastewater until removed, while the liquid flows continuously through the outlet or partition below the water lines. Removes oils, greases, etc.
Aeration Tank:
In this section in wastewater treatment plants, the air is used to remove the solid particles and oil and greasy materials.
Primary Treatment:
In Primary treatment, the sedimentation process is used for most of the solids that can be settled are physically separated or removed from the wastewater. When some chemicals are used in primary sedimentation tanks, some of the mixtures of solids(colloidal) are also eliminated from wastewater.
The process of primary treatment in the sewage treatment plants is used to reduce the pace of the wastewater necessarily to permit solids to settle and floatable the material to the surface. That’s why, primary devices may contain settling tanks, clarifiers, or sedimentation tanks. Because of variations in design, operation, and application, settling tanks can be divided into the following groups:
Sedimentation/Clarification Tank:
In Sewage treatment plant, this tank as name presents, the solid particles are allowed to settle down based on gravity. This process does take some time. This process is also used to slow down the speed of the waste water flow.

Flocculation Tank:
A flocculent (chemical substance) is added in wastewater in the sewage treatment plant to increase the settling speed. Small particle based on charge combine together and create large particles known as flocs and settle down based on gravity.

ETP Equalization Tank:
The function of ETP equalization tanks is not only to act as holding tanks to help balance flow in sewage treatment plant processes but to also act as excellent holding zones for other liquids, agents, and chemicals added in the wastewater treatment systems. Aeration might be required to maintain the wastewater in the original phase during holding time.

Neutralization Tank:
The most critical stage in most of the industrial wastewater treatment processes is the process of Neutralization. It is critical to neutralize the wastewater before going to biological process otherwise it could kill the bacteria or plants
Secondary Treatment/Biological Treatment:
The secondary treatment process depends significantly on the aerobic organisms which biochemically degrade the organic materials to inorganic or stable organic solids. It is similar to the recovery zone in the self-purification of a stream.
Secondary treatment removes dissolved and suspended biological matter. This is typically performed by indigenous, water-borne micro-organisms in a managed habitat. This process may require a separation process to remove the micro-organisms from the treated water prior to discharge or tertiary treatment.
Activated Sludge Process:
It is a type of wastewater treatment process for treating wastewater using aeration and a biological floc composed of bacteria and protozoa. The method of Activated-sludge, is a process in which sludge, the stored, bacteria-rich collections of settling tanks and basins, is spread on the incoming waste water and the combination is stirred for numerous hours in the presence of appropriate air supply.

Trickling Filter:
Organic matter from wastewater is removed by using trickling filters. The TF is an aerobic treatment system that utilizes microorganisms attached to a medium to remove organic matter from wastewater.
A bed of solid media on the surface of which bacteria are attached is trickling filer. Wastewater is irrigated on solid media. It is also known as a biological filter to make it clear that it’s not a mechanical process.

Aerated Lagoons:
The aerated lagoon (or aerated pool) could be simply an effluent treatment system consisting of a pond with artificial aeration to endorse the biological oxidation of wastewaters. The Aeration process increases the efficiency of the treatment process, which can reduce energy costs in some cases. Lagoons with aeration systems need less land area and shorter detention times.
Large cement tanks having 3-5 m depth. The effluent coming from Primary Treatment is stored in these tanks for the duration of 2-6 days which is then aerated mechanically. After aeration for 2-6 days, a healthy sludge in flocculent form is made, which performs the oxidation of organic matter. It can remove up to 90% of BOD.
Oxidation Pond:
An oxidation pond is a large shallow pond. The stabilization of organic matter is brought out by bacteria. Oxygen is required for this purpose of metabolism and is supplied by algae. The algae utilize the carbon dioxide released by bacteria for photosynthesis.
For effective treatment:
- Maximum sunlight penetration (for photosynthesis),
- Wind action for mixing
- Neutral Aeration
Tertiary Treatment:
Tertiary treatment in effluent treatment plant (ETP) is the final treatment, meant for ‘polishing’ the affluent and removal of pollutants not removed in previous treatment processes. These pollutants may include soluble inorganic compounds such as phosphorous or nitrogen which may support algae growth in receiving waters. Tertiary treatment also removes organic materials that contribute to color, taste, odor, bacteria, viruses, BOD, COD, or other soluble minerals that can interfere with the ultimate re-use of the wastewater. Preferred when treated water is needed to be reused or discharged is into the ecosystem.
It produces high-quality effluent which can be reused further for commercial and industrial applications. Treated water can be reused for the irrigation of a golf course, greenway or park, construction work, industrial process, etc. If the water is satisfactorily clean then it can also be used for the recharge of groundwater. Sometimes, the treated water is disinfected by chemicals or physically depending on the location of discharge.
Sand Filters
The Sand Filters are specifically designed to remove additional Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) and Suspended Solids (SS) from sewage and Effluent treatment plant (ETP). This low cost and low maintenance sand filter tertiary treatment technique is an ideal addition for new and existing (permanent or temporary) process units. Sand filters have the capacity to produce high-quality water without even using chemicals additives. Passing flocculated water through a rapid gravity sand filter strains out the floc and the particles trapped within it, reducing numbers of bacteria and removing most of the solids. The sand of varying grades is used as the medium for the filters
Activated Carbon Filters
It is used in effluent treatment plants (ETP) to remove micropollutants or difficult contaminants from industrial effluents. Carbon filtering is a method of filtering that utilizes a bed of activated carbon to remove pollutants and impurities, using chemical absorption. Each particle/granule of carbon provides a large surface area/pore structure, allowing contaminants the maximum possible exposure to the active sites within the filter media.

Disinfection
The killing or removal of pathogenic microorganisms or their deactivation is known as water disinfection. Destruction or deactivation of microorganisms results in the closure of their reproduction and growth. Physical or chemicals disinfectants are means through which disinfection can be achieved.
Chemical Disinfection:
- Chlorine
- Chlorine dioxide
- Ozone
- Several acids and bases etc.
Physical Disinfection
Ultraviolet light (UV)
- Electronic radiation
- Gamma rays
- Sounds
- Heat
Ion-Exchange
The exchange of irons between an electrolyte solution, and a complex or between two electrodes is called ion exchange.
The term ion exchange is significantly used in the case of the purification process, decontamination, or separation of aqueous and other solutions that contain ions with the use of solid or mineral ion exchangers.
Through this process, it is possible to regenerate resins. It has a low initial cost. The ion exchange method is extensively used to remove hardness, iron, and magnesium salts. But it does not remove bacteria effectively.
This process is most commonly used to recover H2SO4, Cu, Pb, Hg, Cr, Ni, and also the removal of cyanides after recovery of Cr. from wastewater Majorly used for recovery of Cr, Ni, Phosphate and H2SO4, Cu, Pb, Hg and removal of cyanides from wastewater after Cr recovery.


Thanks for the post-Voice of Environment team. I am amazed, how you explained the Effluent Treatment plant process very well. We provide services for all types of water treatment solutions if any query please visit our website.
LikeLike